Scientific Evidence: Ivermectin is Effective Against COVID-19
There is scientific proof that Ivermectin, FDA Approved for humans, is effective at preventing and treating COVID-19.
If you don’t want to read through the study abstracts below, here are the bottom-line conclusions of each:
- “Two-dose ivermectin prophylaxis at a dose of 300 μg/kg with a gap of 72 hours was associated with a 73% reduction of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers for the following month. Chemoprophylaxis has relevance in the containment of pandemic”
- “A 5-day course of ivermectin was found to be safe and effective in treating adult patients with mild COVID-19.”
- “We report here that Ivermectin, an FDA-approved anti-parasitic previously shown to have broad-spectrum anti-viral activity in vitro, is an inhibitor of the causative virus (SARS-CoV-2)”
- “Treatment with ivermectin in a population of outpatients with COVID-19 mild disease managed to significantly reduce the number of symptoms”
- “Treatment with ivermectin could significantly prevent the evolution to serious stages”
This image contains the percentage of improvement seen in patients from 44 peer-reviewed studies with an average of 70% improvement over not treating with ivermectin:
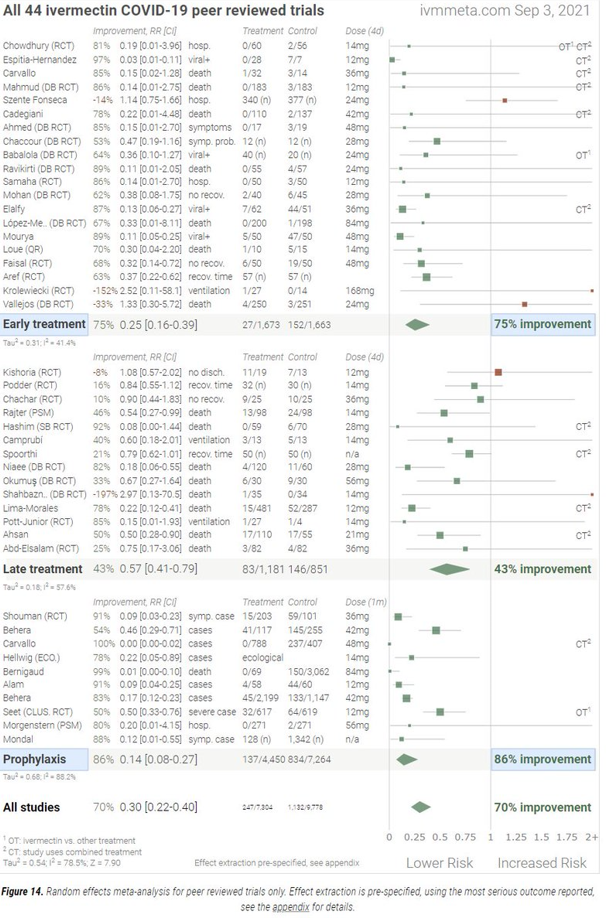
Once anyone has seen the analysis above or the studies below, the biggest question remaining is why isn’t ivermectin used prophylactically for the most at-risk and as part of the treatment for anyone with symptoms and a positive COVID test? Why???
Maybe because Pfizer has a new SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitor (as ivermectin has been proven to be) in drug trials and would rather everyone pay tons more than they would for the generic, and available now, ivermectin.
The next time you hear or see someone alleging that there is no scientific evidence that Ivermectin is effective at treating SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, or that it’s only a horse dewormer, show them these scientific studies:
Study 1: Role of ivermectin in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers in India: A matched case-control study
Priyamadhaba Behera 1, Binod Kumar Patro 1, Arvind Kumar Singh 1, Pradnya Dilip Chandanshive 1, Ravikumar S R 1, Somen Kumar Pradhan 1, Siva Santosh Kumar Pentapati 1, Gitanjali Batmanabane 2, Prasanta Raghab Mohapatra 3, Biswa Mohan Padhy 4, Shakti Kumar Bal 3, Sudipta Ranjan Singh 5, Rashmi Ranjan Mohanty 6Affiliations expand
- PMID: 33592050
- PMCID: PMC7886121
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247163
Free PMC article
Abstract
Background: Ivermectin is one among several potential drugs explored for its therapeutic and preventive role in SARS-CoV-2 infection. The study was aimed to explore the association between ivermectin prophylaxis and the development of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers.
Methods: A hospital-based matched case-control study was conducted among healthcare workers of AIIMS Bhubaneswar, India, from September to October 2020. Profession, gender, age and date of diagnosis were matched for 186 case-control pairs. Cases and controls were healthcare workers who tested positive and negative, respectively, for COVID-19 by RT-PCR. Exposure was defined as the intake of ivermectin and/or hydroxychloroquine and/or vitamin-C and/or other prophylaxis for COVID-19. Data collection and entry was done in Epicollect5, and analysis was performed using STATA version 13. Conditional logistic regression models were used to describe the associated factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Results: Ivermectin prophylaxis was taken by 76 controls and 41 cases. Two-dose ivermectin prophylaxis (AOR 0.27, 95% CI, 0.15-0.51) was associated with a 73% reduction of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers for the following month. Those involved in physical activity (AOR 3.06 95% CI, 1.18-7.93) for more than an hour/day were more likely to contract SARS-CoV-2 infection. Type of household, COVID duty, single-dose ivermectin prophylaxis, vitamin-C prophylaxis and hydroxychloroquine prophylaxis were not associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Conclusion: Two-dose ivermectin prophylaxis at a dose of 300 μg/kg with a gap of 72 hours was associated with a 73% reduction of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers for the following month. Chemoprophylaxis has relevance in the containment of pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Study 2: A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness
Sabeena Ahmed 1, Mohammad Mahbubul Karim 1, Allen G Ross 1, Mohammad Sharif Hossain 1, John D Clemens 1, Mariya Kibtiya Sumiya 1, Ching Swe Phru 1, Mustafizur Rahman 1, Khalequ Zaman 1, Jyoti Somani 2, Rubina Yasmin 3, Mohammad Abul Hasnat 4, Ahmedul Kabir 5, Asma Binte Aziz 1, Wasif Ali Khan 6Affiliations expand
- PMID: 33278625
- PMCID: PMC7709596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.191
Free PMC article
Abstract
Ivermectin, a US Food and Drug Administration-approved anti-parasitic agent, was found to inhibit severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) replication in vitro. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted to determine the rapidity of viral clearance and safety of ivermectin among adult SARS-CoV-2 patients. The trial included 72 hospitalized patients in Dhaka, Bangladesh, who were assigned to one of three groups: oral ivermectin alone (12 mg once daily for 5 days), oral ivermectin in combination with doxycycline (12 mg ivermectin single dose and 200 mg doxycycline on day 1, followed by 100 mg every 12 h for the next 4 days), and a placebo control group. Clinical symptoms of fever, cough, and sore throat were comparable among the three groups. Virological clearance was earlier in the 5-day ivermectin treatment arm when compared to the placebo group (9.7 days vs 12.7 days; p = 0.02), but this was not the case for the ivermectin + doxycycline arm (11.5 days; p = 0.27). There were no severe adverse drug events recorded in the study. A 5-day course of ivermectin was found to be safe and effective in treating adult patients with mild COVID-19. Larger trials will be needed to confirm these preliminary findings.
Keywords: Bangladesh; COVID-19; Doxycycline; Ivermectin; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work described in this paper.
Figures

Report: The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro
Leon Caly 1, Julian D Druce 1, Mike G Catton 1, David A Jans 2, Kylie M Wagstaff 3Affiliations expand
- PMID: 32251768
- PMCID: PMC7129059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Free PMC article
Abstract
Although several clinical trials are now underway to test possible therapies, the worldwide response to the COVID-19 outbreak has been largely limited to monitoring/containment. We report here that Ivermectin, an FDA-approved anti-parasitic previously shown to have broad-spectrum anti-viral activity in vitro, is an inhibitor of the causative virus (SARS-CoV-2), with a single addition to Vero-hSLAM cells 2 h post infection with SARS-CoV-2 able to effect ~5000-fold reduction in viral RNA at 48 h. Ivermectin therefore warrants further investigation for possible benefits in humans.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Ivermectin Repurposing For COVID-19 Treatment Of Outpatients With Mild Disease In Primary Health Care Centers
Abstract
Background The emergency of COVID-19, along with the current difficulties in responding to the high demand for vaccines, requests to the scientific community to find alternative treatments based on reuse of drugs as a strategy to prevent the progression of the disease in patients infected with SARS COV 2. This study aims to evaluate the use of ivermectin in mild-stage patients to increase outpatient discharge and prevent the progression to moderate or severe stages of the disease.
Methods Cluster Randomised Trials in outpatients care, n = 254. The subjects were divided into experimental (EG: n = 110) and control groups (CG: n = 144). The EG received ivermectin orally 4 tablets of 6 mg = 24 mg every 7 days for 4 weeks. All participants were diagnosed by positive RT-PCR for COVID-19 and were evaluated by clinical examination, at the beginning and the end of protocol. Data analyzed using proportion, bivariate and logistic regression. P-value was considered significant at the p < 0·05 threshold. This study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT04784481.
Findings Both groups were similar in age, sex, and comorbidities (EG: median age = 40·0, range: 18·0–75·0, 42·11% Female; CG: median age = 36, range: 18·0–71·0, 57·89% Female). A significant reduction in the percentage of participants with symptoms (PPS) was observed in the EG and CG when the clinical evaluation of symptoms was performed from 5th to 9th (p = 0·0005). When the clinical evaluation was performed from 10th to 14th day there was no significant difference. A higher proportion of outpatient discharge was observed in EG (98·2%) vs. CG (86·1%) (p-Value = 0·0007). EG showed 8 times more chance of receiving discharge than CG (8·71 CI = [1·99, 38·12]; p = 0·004). The treatment effect with ivermectin to obtain discharge from outpatient care was analyzed by the logistic regression. Then, the chance to obtain outpatient discharge was independent of variables sex, age, and comorbidities.
Interpretation Treatment with ivermectin in outpatients care with mild disease of COVID-19 managed to slightly reduce PPS. Also, this treatment improved the clinical state to obtain outpatient discharge, even in the presence of comorbidities. The treatment with ivermectin could significantly prevent the evolution to serious stages since the EG did not present any patient with referral to critical hospitalization.
Content created by Conservative Daily News and some content syndicated through CDN is available for re-publication without charge under the Creative Commons license. Visit our syndication page for details and requirements.




