Lyme Disease Prevalence Increasing in U.S.
- Number of positive tests for Lyme disease increased significantly between 2016 and 2017
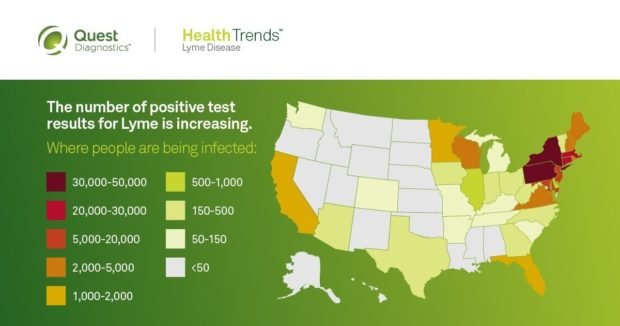
- Historically concentrated in Pennsylvania and New England states, Lyme disease has been detected in each of the 50 United States and the District of Columbia
- Outside of the northeastern U.S., California and Florida – states not historically associated with significant rates of Lyme disease – saw the largest absolute increases in positive Lyme disease test results
- Notable increases also observed in Georgia, Arizona, Ohio, Texas, Tennessee and Virginia
The prevalence of Lyme disease is increasing in the United States, spiking significantly between 2016 and 2017, and has spread to all 50 United States and the District of Columbia, according to a new study released today by Quest Diagnostics (NYSE: DGX).
Based on more than six million de-identified laboratory test results conducted over the past seven years, the Quest Diagnostics study also found that outside of the northeastern U.S. which is historically associated with Lyme disease, California and Florida saw the largest absolute increases in positive test results. California found 483 infected patients in 2017, a 194.5 percent increase over 2015 levels. Floridafound 501 infected patients in 2017, a 77 percent increase over 2015 levels.
“Lyme disease is a bigger risk to more people in the United States than ever before,” said Harvey W. Kaufman, M.D., senior medical director for Quest Diagnostics and head of the company’s Health Trends research program. “Our data show that positive results for Lyme are both increasing in number and occurring in geographic areas not historically associated with the disease. We hypothesize that these significant rates of increase may reinforce other research suggesting changing climate conditions that allow ticks to live longer and in more regions may factor into disease risk.”
To access the full report, go to: www.QuestLymeReport.com
The Quest Diagnostics Health Trends™ report on Lyme disease is the latest in a series of reports from Quest providing insights derived from the company’s 44 billion de-identified laboratory test results, the largest database of clinical lab results in the word. These reports are intended to provide actionable insights that can improve health outcomes for conditions affecting a large number of Americans. Additional findings of the Quest Diagnostics Health Trends report on Lyme disease include:
- Lyme disease remains most prevalent in the Northeastern United States Combined, Pennsylvania and the six New England states (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont) accounted for 60.6 percent of the total number of positive Lyme disease test results found in the United States in 2017.
- Pennsylvania tops the nation in Lyme disease cases. With 10,001 cases in 2017, Pennsylvaniasaw the most positive Lyme disease test results of any state in the nation, and nearly as many found in all New England states combined (11,549).
- Notable increases also observed in other states between 2015 and 2017 including Georgia, Arizona, Ohio, Texas, Tennessee, and Virginia.
Spread by tick bites from infected blacklegged and deer ticks, Lyme disease is an infection by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi that causes more than 300,000 illnesses each year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). It is the most commonly occurring vector-borne disease and the sixth most commonly reported notifiable infectious disease.
Common signs of potential Lyme exposure include the tell-tale “bullseye” shaped mark that frequently forms on the skin at a tick-bite location, or a presence of flu-like and/or other symptoms associated with Lyme or tick-borne infections.
Unique Test from Quest Helps Diagnose Tick-Borne Diseases
Physicians who suspect their patients might have been exposed to the bacteria causing Lyme disease can order laboratory tests to confirm the presence of Lyme or other tick-borne diseases. The Quest Diagnostics Health Trends™ report analyzes results of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody testing. This immunoblot test can help identify antibodies produced by the body in response to infection.
In recent years, other tick-borne diseases have emerged in addition to Lyme disease. These conditions may share common symptoms but require different therapies, challenging accurate diagnosis and outcomes. This summer, Quest introduced a new test service that helps identify infection of Lymedisease and four other tick-borne infections from a single patient specimen. This test uses advanced technologies, including qualitative real-time PCR, to identify the DNA of each infectious agent. Quest also offers a test that detects antibodies and if positive or equivocal is confirmed by immunoblot.